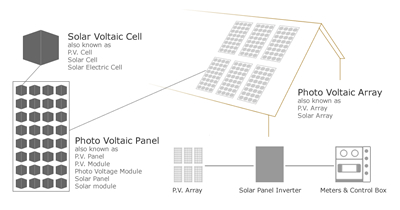
Solar ElectricitySunlight is a limitless resource that is never going to stop shining. In just one minute there is enough solar energy reaching the earth from the sun to meet the worlds total energy requirements for a whole year! Special solar cells called Photovoltaic Cells or ‘PV’ Cells are able to convert sunlight into electricity. Solar electricity systems capture energy from the sun to produce electricity that can be used to power household appliances, heating and lighting. Photovoltaic panels only require light in order to produce electricity. PV panels are commonly used to provide small amounts of electricity and are often found providing power for calculators, phone chargers, watches, road signs and alarm systems. By using large PV panels or by linking a number of panels together, greater amounts of electricity can be produced in order to power household appliances, heating and lighting. These panels are commonly mounted on top, or integrated into, the roof of your home. There are many different types of PV panels and PV arrays available in a variety of shapes, sizes and colours. In addition to basic panels they are available as solar tiles that look similar to roof tiles and even transparent sheets that can be installed on conservatory roofs. PV panels and PV arrays are made to withstand the outside elements and because they have no moving parts they are usually guaranteed to last for 20 to 25 years and often have a life expectancy of more than 50 years.
Solar energy being used to generate electricity is a relatively new technologyA series of important discoveries led to the development of solar cells that could generate electricity: Photovoltaic effect In 1839 the photovoltaic effect was first recognised by a 19 year old French physicist A E Becquerel. Photovoltaic means ‘light electric’, coming from the Greek word ‘phos’ that means light and ‘voltaic’ taken from the name of the physicist ‘Volta’ whom the electrical unit ‘volt’ is name after, to represent electric. In 1905 Albert Einstein explained the photovoltaic effect for which in 1921 he received the Nobel Prize for Physics.
Conductivity properties of selenium Whilst developing the first telegraph system between Europe and America in the 1860s a discovery was made about the properties of the trace mineral selenium. It was discovered that the conductivity of selenium can increase by as much as 1000 times when sunlight shines on it, compared to when it is kept in darkness.
Silicon used to generate electricity from sunlight In the 1950s it was discovered that by using silicon to build transistors in a certain way it was possible to make a solar cell that can generate a small amount of electricity. By putting a number of these cells together in a panel, enables a larger and more useful amount of electricity to be generated.
Endless power for the Space Industry In the early days of photovoltaic panels it was hugely expensive to make a panel, so due to this cost there was no commercial demand for them. That changed when PV panels became the solution to providing satellites in space with an endless source of power. Thanks to the space industry PV panels quickly developed becoming increasingly advanced. The development of PV panels was further boosted by the increase in demand for renewable energy in the 1960s, the oil crisis of 1973, then again in 1979/80. Today PV panels are quickly growing in popularity and the demand for them is growing by as much as 80% each year.
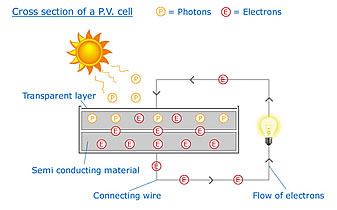
How a PV cell worksPV cells are made from semi-conducting materials, most commonly this is silicon. When exposed to light PV cells create electricity by making use of the photovoltaic effect. Sunlight is made up of tiny packets of energy called photons. When PV cells are exposed to light they are able to absorb photons. These photons excite the atoms in the semi-conducting materials and cause them to move to the bottom of the PV cell where they exit through the connecting wire. This flow of electrons is known as electricity. They are referred to as cells because like power cells, more commonly known as batteries, they produce Direct Current (DC) electricity. A single PV cell only produces a small amount of electricity, so by putting a number of these cells together into a panel, larger and more useful amounts of electricity can be produced.
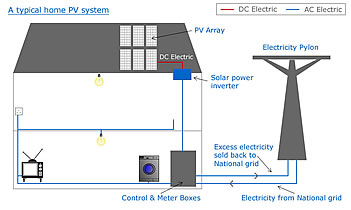
PV systems to produce electricity for your homeMain components that make up a PV system are the: PV Array A PV array is made up of a number of PV panels that are linked together. The number of panels used to make the array will depend on the amount of solar electricity required. PV arrays are commonly roof mounted using frame like structures made from aluminium and/or stainless steel, so that they are hardwearing and weatherproof. Alternatively the panels can be roof integrated so that they blend in better by sitting flush with the roof line. Due to the demand for less conspicuous panels, PV panels that look like roof tiles in addition to glass panels that can be placed in conservatory roofs, are available. Solar Power Inverter The PV array produces DC electricity but the national grid provides a home with AC electricity to power household appliances, lights and heating systems that are designed to use AC electricity. A solar power inverter is used to convert the DC electricity produced by the PV panels into AC electricity. Automatic Control and Metre Box The AC electricity from the inverter is then connected into the electrical system at the house. An automatic control and metre box manages, distributes and records the solar electricity produced, used and sold back to the national grid. During the daytime electricity will be produced and this will provide the property with electricity. If the property requires more electricity than the PV system is producing the shortfall will be met by electricity from the national grid. However any excess electricity produced that is not required by the property can be sold back to the national grid. Therefore someone else can benefit from the green electricity that you have produced, in addition to you receiving payment for it. Batteries For properties that do not have connection to the national grid PV systems usually make use of batteries to store any excess power produced. Then at times of high demand or at night the batteries can feed back the electricity that they have stored.
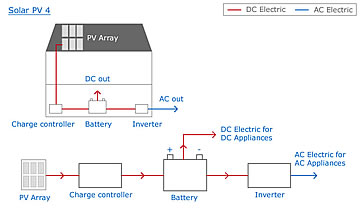
Types of PV systemGrid Connected systems These systems are the most popular and most common for homes and businesses in the UK. The systems are connected to the national grid so that any electricity produced that is not required can be fed back into the national grid and sold. During times when more electricity is required than the system is producing, electricity can be drawn from the national grid to meet the shortfall. Off Grid Systems These systems are not connected to the national grid and are popular for properties in remote locations without any connection to the national grid. They are also found in properties who have connection to the national grid but have chosen to operate their PV system as an off grid system. In off grid systems the electricity produced by the PV array is used to charge batteries. These batteries will provide DC electricity for lights and appliances and can also be connected to an inverter to provide power for any appliances that require AC electricity. Hybrid systems Hybrid systems can be grid connected, grid support or stand alone. The PV system will work in combination with other sources of power such as a wind turbine, CHP boiler, and/or a petrol, diesel or biomass generator. The combination of power sources helps to ensure a constant supply of electricity.
What are the best PV panels?PV systems are measured in units known as kilo watts peak or kWp. This provides information about how much power a panel or system can generate under standard test conditions. The efficiency of a panel is calculated by measuring its power output when exposed to 1 kW (kilo watt) of light for every square metre of panel area. Therefore if a panel with an area of 1 square metre has a power output of 0.2 kW when exposed to 1kW of light, it has converted 20% of the light reaching it into electricity. This would mean that the panel is 20% efficient. The best domestic PV panels are around 22% efficient. The more efficient a panel or system is, the smaller the area required to produce the required amount of electricity. A 20% efficient PV system will require half the panel area as a 10% efficient system to produce the same amount of electricity. Crystalline silicon Crystalline silicon is most commonly used in the UK, and this technology is made use of in two different ways: Monocrystalline silicon PV cells contain thin slices of silicon that have been cut from a single crystal. Panels made using monocrystalline silicon are the most efficient, having efficiencies ranging from 15% to 21.5%. They also tend to be the most expensive. Polycrystalline silicon PV cells contain thin slices of silicon that have been cut from a block of crystals. Panels made using polycrystalline silicon have efficiencies ranging from 8% to 12% Thin film PV cells Thin film PV cells are commonly used for the mass production of PV cells and are therefore cheaper to produce. They are made using thin layers of photosensitive materials that are placed onto glass, plastic or stainless steel. The photosensitive materials used are: Amorphorous silicon – having efficiencies of around 5% to 6% Cadmium telluride – having efficiencies around 7% Copper indium diselenide – that has efficiencies around 9%
MaintenanceMaintenance of PV systems is normally very small as they are no moving parts and the PV array outside is made of very durable and long lasting materials. The only maintenance required is to keep the panels clean and dust free so that they can absorb as much sunlight as possible. Most panels have a transparent glass surface with self cleaning properties, so keeping them clean isn’t difficult. Snow on solar panels Snow will tend to stick to the surface of PV panels and stay there until their temperature rises enough to melt the snow. Light reaching the PV cells is restricted through snow so electricity production will be decreased. However when it is sunny light can still reach the PV cells because snow transmits diffused light. Unfortunately if the snow becomes quite thick light will be completely blocked and no electricity will be produced. On the bonus side though, due to the lower temperatures the PV panels will have improved efficiency! If you can easily and safely reach your PV panels then you can clear the snow. Be careful not to use anything to clear the snow that could damage your PV panels. Also, if there is any safety risk in reaching your panels, for example using a ladder in slippery conditions, please just leave them because it is just not worth the risk!
ConsiderationsPlanning permission – Most domestic solar panel systems are considered permitted development in England and Wales. Therefore they don't require planning permission provided that the solar panels are not installed above the ridgeline of the roof on your home. However it is always best to consult your local planning office, especially if you live in any of the following, because restrictions may apply:
Direction that the PV panels should face – PV panels are best positioned facing due south. However, they are still very effective facing anywhere between east through south to west. Where to position solar panels – Solar panels are most usually mounted on the roof of your home or garage and you will need about 10 square metres of roof space that receives direct sunlight. They can also be mounted at ground level, but it is important that they collect direct sunlight and are not positioned where their performance may be reduced by shadows from trees, buildings, telegraph poles, etc. Weight of the solar panels – The solar panels are not lightweight so make sure that your roof or any other structure that you intending to mount your panels on are strong enough. If the panels are to be placed above existing roof tiles special care should be taken to ensure that your roof if strong enough. Best angle for solar panels – To obtain the best performance from solar panels they should be positioned at an angle of between 30° and 40°, although reasonable levels of sunlight can be captured at angles down to 20° and up to 50°. Most pitched roofs usually provide a suitable pitch angle, but brackets should be used in order to achieve the best operational angle when being installed on flat roofs. What size system do I require? – Domestic solar power systems range from 1 to 5 kWp. Any excess electricity produced by the system that isn’t used can be sold back to the national grid. Amount of solar panels required – You will require about 8 square metres of PV panels for 1 kWp. Is connection to the national grid available – Provided that you are intending to sell any surplus electricity back into the national grid, you will need to ensure that you can obtain a suitable connection that will allow you to feed your surplus electricity back into the grid. Most properties that receive their electricity from the national grid will be able to feed back any surplus electricity that they produce. Electricity suppliers – Most electricity suppliers will buy back electricity that has been generated by domestic solar panels. The amount that the suppliers are prepared to pay per kilowatt does vary so it is best to shop around for the best deal.
Benefits and Advantages of Solar ElectricityReduce your energy bills – any electricity produced using energy from the sun is free. PV systems work best on sunny days when direct sunlight is shinning on the PV panels, but even on cloudy and dull days they can produce significant amounts of electricity. Receive payment for the electricity that you produce – If your system is grid connected under the feed in tariff scheme you will receive a guaranteed payment for every kilowatt of electricity that you generate. This payment will be increased for every kilowatt that you generate and sell back to the national grid. Cut your carbon footprint – the sun is a completely renewable energy therefore electricity generated using solar energy is free from carbon emissions. Solar energy maybe the only renewable option available – The most suitable renewable energy for the vast majority of homes in the UK is solar power. To make use of hydropower a property needs to have access to a suitable stream or river. Wind power requires access to an exposed area that is at least 300 metres from the nearest neighbour. Solar panels can be installed on the roof of most houses in the UK. Silent – Unlike other methods of generating electricity from renewable energy, PV systems are silent. Low maintenance – PV electric systems require very little maintenance. It is important that they are kept clean from dirt and dust so that they provide their best performance, and this is aided by the glass on the top side of most PV panels being self cleaning. Branches from trees and anything else that could cause shadows and restrict sunlight from reaching the PV panels should be monitored and controlled. Easily expandable – Once you have a PV system it is easily expandable to produce more electricity by simply adding more PV panels to your PV array, or adding an additional PV array somewhere else on your property. Grants – Government grants are available to help you cover the cost of buying and installing a PV electric system. Long Lifetime – Most systems have a 20 or 25 year guarantee and a correctly installed system can last for 50 years or more. Increase the value of your house – Due to their desirability installing solar panels can increase the value of your property.
more here
|